How to Start a Millet Export Business
Thinking of Millet Export Business? Learn the steps, regulations, and opportunities in this growing market!
Introduction
The global demand for healthy and organic food products is on the rise, and millets have gained significant traction as a superfood. The millet export business offers lucrative opportunities for entrepreneurs looking to tap into the international market. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to starting and growing a successful millet export business.

To start a millet export business, begin by researching international demand, target markets, and export regulations. Obtain necessary certifications like FSSAI, APEDA, and organic certifications if applicable. Establish connections with reliable millet farmers or suppliers to ensure quality and consistent supply. Set up a processing unit for cleaning, grading, and packaging to meet global standards. Register your business, acquire an Import-Export Code (IEC) from DGFT, and comply with export documentation requirements. Develop a strong online presence and network with international buyers through trade fairs, B2B marketplaces, and export promotion councils. Secure reliable logistics partners for smooth shipping and maintain quality control to build a trusted brand.
Understanding the Millet Export Business
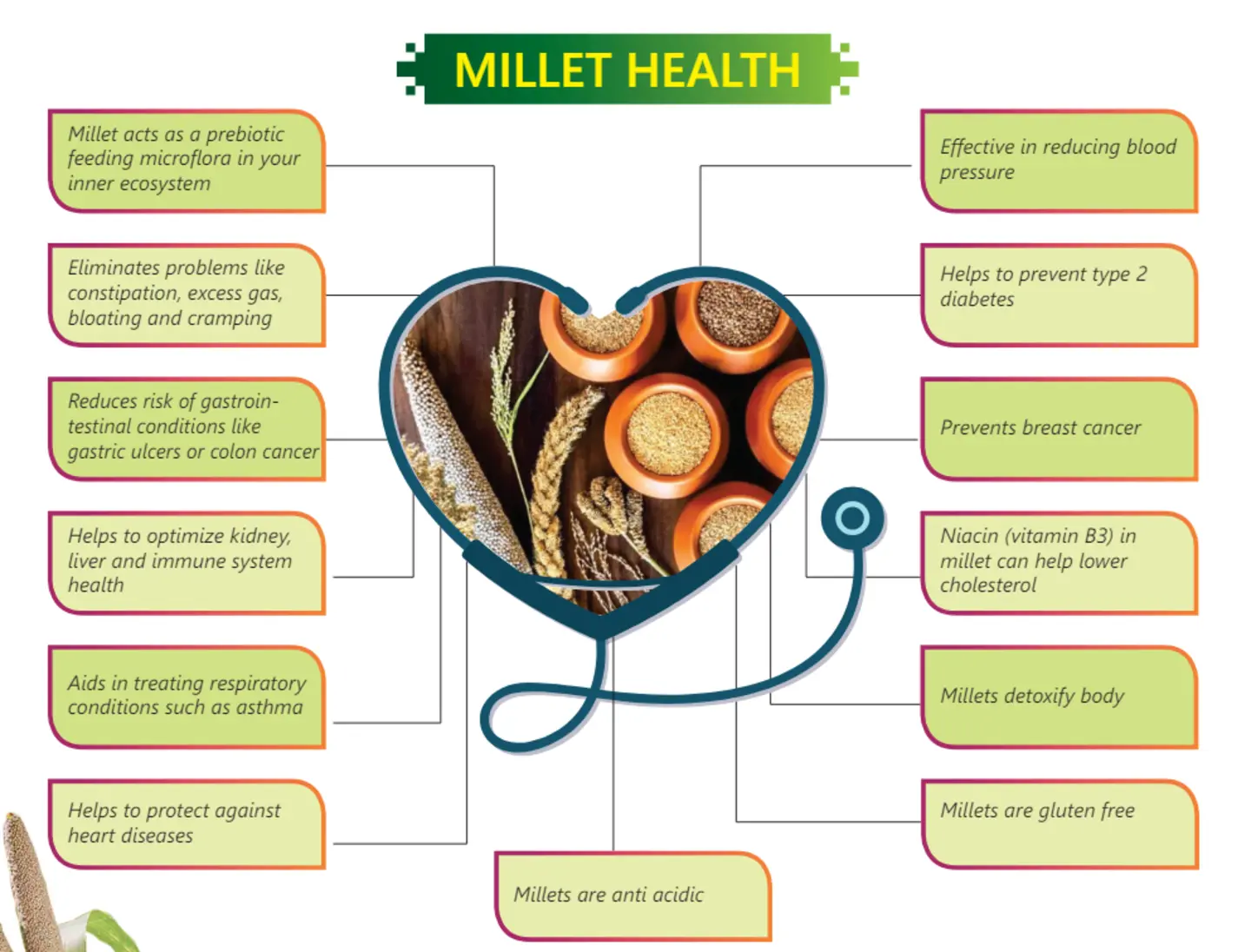
Millets are gluten-free, nutrient-dense grains that have been a staple food in many regions for centuries. The increase in health-conscious consumers, coupled with government initiatives promoting millet farming, has made the millet export business highly profitable. Countries like the USA, UAE, Japan, and European nations have a growing demand for Indian millets.

1. Growing Global Demand for Millets
Millets are becoming a staple in many countries due to their rich nutritional profile and gluten-free nature. The demand for these grains has surged in health-conscious markets such as the USA, Europe, and the Middle East. As a result, the millet export business has become a lucrative opportunity for farmers and traders looking to expand their reach beyond domestic markets.
2. India’s Position in Millet Exports
India is one of the leading producers of millets, contributing significantly to global supply. With government initiatives like the “International Year of Millets 2023” and export-friendly policies, the millet export business is gaining momentum. Countries like the UAE, USA, Germany, and Japan are key importers of Indian millets.
3. Types of Millets for Export
Different varieties of millets are exported, including Pearl Millet (Bajra), Finger Millet (Ragi), Foxtail Millet, Sorghum (Jowar), and Barnyard Millet. Each type has unique nutritional benefits and is used in different food applications, such as bakery products, health supplements, and traditional dishes.
4. Quality Standards and Certification
To enter the millet export business, exporters must meet international quality standards. Certification from agencies such as FSSAI, APEDA, USDA Organic, and EU Organic is crucial. These certifications ensure that the millets are free from harmful chemicals and meet global food safety regulations.
5. Processing and Packaging Requirements
Exporting millets requires proper processing, cleaning, and packaging to meet international quality standards. Modern packaging techniques such as vacuum sealing and nitrogen flushing help in preserving freshness. Attractive and informative labeling, including details about nutritional value, country of origin, and expiry dates, is essential for successful exports.
6. Finding International Buyers
Identifying the right buyers is key to success in the millet export business. Exporters can use B2B platforms like Alibaba, TradeIndia, and Export Genius to connect with potential buyers. Participating in international trade fairs and networking with food importers also helps in establishing strong business relationships.
7. Export Regulations and Documentation
Exporting millets requires proper documentation, including an Importer-Exporter Code (IEC), phytosanitary certificate, certificate of origin, and customs clearance. Understanding trade agreements and tariff structures for different countries ensures smooth shipment without unexpected costs.
8. Logistics and Shipping Considerations
Choosing the right logistics partner for millet exports is crucial. Factors such as shipping methods (air, sea, or land), freight costs, and storage conditions affect profitability. Maintaining proper warehouse facilities and ensuring timely deliveries help in gaining customer trust and expanding market reach.
9. Challenges in the Millet Export Business
Despite its potential, the millet export business faces challenges such as fluctuating market demand, stringent import regulations, and competition from other grain-exporting countries. Weather conditions and inconsistent yield can also impact the availability of millets for export.
10. Future Prospects of Millet Exports
With increasing awareness about millets and their health benefits, the future of the millet export business looks promising. Innovations in millet-based products, government incentives, and collaborations with international buyers can further boost India’s position in the global millet market.
Market Research and Demand Analysis
1. Global Demand for Millets
Millets are exported to various international markets where consumers seek organic and nutrient-rich food options. Key importers include:
- USA
- Canada
- UAE
- European Union
- Japan
Millets, once considered a staple for traditional diets in specific regions, have gained immense global popularity due to their numerous health benefits and sustainable cultivation practices. The increasing awareness of organic and nutrient-rich food options has fueled the demand for millets in various international markets. Countries such as the USA, Canada, the UAE, the European Union, and Japan are emerging as key importers, recognizing the value of these ancient grains.
Overview of Millet Demand in Global Markets
Millets are recognized for their high nutritional value, including being rich in fiber, protein, and essential minerals such as iron, calcium, and magnesium. They are gluten-free and have a low glycemic index, making them suitable for people with diabetes and those following gluten-free diets. Additionally, the shift toward plant-based diets has propelled their demand among health-conscious consumers worldwide.
With the rise of lifestyle diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions, consumers are actively seeking healthier grain alternatives. Millets have been incorporated into diverse food products such as millet flour, millet-based snacks, breakfast cereals, and energy bars. This diversification has contributed to their acceptance in global markets.
USA: A Booming Market for Millets
The USA has seen a significant rise in demand for millets due to the growing preference for organic and whole foods. The surge in vegan and gluten-free diets has positioned millets as a viable alternative to conventional grains like wheat and rice. The increasing popularity of millet-based products, including flour, noodles, and ready-to-eat snacks, has attracted major food companies and retailers.
Moreover, government initiatives promoting sustainable and healthy eating habits have further boosted the demand. The US market also benefits from e-commerce platforms that make it easier for consumers to access millet products from different parts of the world. Large supermarket chains and organic food stores now stock various millet-based items, making them more accessible to the mainstream population.
Canada: A Growing Market for Millet-Based Products
Canada, known for its diverse food preferences and strong health-conscious consumer base, has been witnessing increased millet imports. Health enthusiasts and fitness-conscious individuals are incorporating millets into their diets due to their rich protein and fiber content. Millets are now available in various forms such as flakes, puffs, and energy bars, which appeal to Canadian consumers.
Additionally, Canada’s cold climate makes it dependent on imported grains, which opens opportunities for millet exporters. As more people adopt plant-based and organic food lifestyles, millet consumption is expected to rise significantly in the coming years.
UAE: Rising Demand for Millets in the Middle East
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has a diverse population, with a significant number of expatriates seeking healthy food alternatives. The demand for gluten-free and diabetic-friendly foods has led to increased millet imports, especially among Indian, African, and Middle Eastern communities.
Supermarkets and organic food stores in the UAE have started stocking millet-based products to cater to the health-conscious population. Moreover, the hospitality sector, including hotels and restaurants, has also incorporated millets into their menus, offering millet-based dishes and bakery products. The growing awareness regarding sustainable food choices has further contributed to the market expansion in the region.
European Union: A Strong Market for Organic Millets
The European Union (EU) has strict regulations regarding food quality and safety, which has increased the demand for certified organic millets. Countries like Germany, France, the UK, and the Netherlands have embraced millets due to their nutritional benefits and sustainable farming practices. The shift towards non-GMO, pesticide-free, and organic foods has significantly boosted the millet market in Europe.
Millet-based products such as organic cereals, pasta, bread, and baby food have gained traction in the EU market. Additionally, the rising popularity of alternative grains for reducing carbon footprints has encouraged European consumers to switch to millets. Food brands are increasingly developing millet-based offerings to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly and nutritious foods.
Japan: A Market Driven by Health and Tradition
Japan has a deep-rooted culture of consuming traditional and health-enhancing foods. With an aging population and increased awareness of preventive healthcare, there is a growing preference for nutritious grains like millets. Japanese consumers appreciate millet’s health benefits, including its ability to improve digestion, control blood sugar levels, and support weight management.
Food manufacturers in Japan have incorporated millets into various products such as rice blends, energy bars, and traditional porridge. The market for functional foods, which promote health benefits beyond basic nutrition, has also contributed to millet’s growing demand in Japan. Additionally, the trend of sustainable and organic farming aligns with Japan’s focus on high-quality, eco-friendly food sources.
Factors Driving Global Demand for Millets
Several factors contribute to the increasing global demand for millets:
-
Health Benefits and Nutritional Value
Millets are packed with essential nutrients such as fiber, protein, iron, calcium, and antioxidants. Their health benefits include improved digestion, better heart health, and blood sugar control, making them a preferred choice among health-conscious consumers worldwide.
-
Growth of Vegan and Gluten-Free Diets
With more people opting for plant-based diets and gluten-free alternatives, millets serve as a nutritious and versatile grain replacement. They cater to dietary restrictions and preferences, making them widely accepted in international markets.
-
Sustainable Farming Practices
Millets require minimal water and grow well in dry, arid conditions, making them a climate-resilient crop. As sustainability becomes a global priority, millets are seen as an environmentally friendly alternative to water-intensive crops like rice and wheat.
-
Rising Demand for Organic and Functional Foods
The increasing awareness of organic food consumption and its health benefits has led to a rise in demand for organic millets. Additionally, functional foods that offer health benefits beyond basic nutrition are gaining popularity, driving millet-based product innovations.
-
Government Initiatives and Support
Several governments and agricultural organizations promote millet cultivation and exports. Countries like India have launched initiatives such as the “International Year of Millets” to boost awareness and consumption worldwide.
Challenges in the Millet Export Business
Despite the rising demand, exporters face challenges such as:
- Strict Import Regulations: Many countries have stringent food safety and certification requirements that exporters must comply with.
- Supply Chain Constraints: Ensuring consistent quality and availability of millets can be challenging due to seasonal fluctuations.
- Market Awareness: While demand is growing, consumer awareness about millet varieties and their benefits still needs further education and marketing efforts.
Future Prospects and Opportunities
The global millet market is expected to witness continued growth, driven by health trends, sustainable agriculture, and increasing awareness. Exporters who focus on quality, certifications, and product innovation can tap into this expanding market successfully. Investing in millet-based processed products, such as flour, snacks, and ready-to-eat meals, can further enhance market penetration.
2. Competitive Landscape
Understanding competitors in the millet export business is essential. Researching market trends, pricing, and supply chain logistics can help exporters position themselves effectively.
Rising Demand for Millets
The demand for millets has grown significantly due to increased consumer awareness of their health benefits. Several factors drive this trend:
- Health Consciousness: Millets are gluten-free, high in fiber, and rich in essential nutrients, making them a preferred choice for health-conscious consumers.
- Government Support: Many governments, including India, are promoting millet production and exports through subsidies, incentives, and branding campaigns. The United Nations also declared 2023 as the International Year of Millets.
- Sustainability Factor: Millets are drought-resistant and require less water compared to other staple crops like rice and wheat, making them an eco-friendly choice.
- Rising Vegan and Organic Diets: The global shift towards plant-based and organic diets has increased demand for millets in markets such as the USA, Canada, and Europe.
Key Export Markets
Major importing countries for millets include:
- USA & Canada: High demand due to the popularity of gluten-free and organic foods.
- European Union: Countries like Germany, France, and the UK have a growing consumer base for healthy grains.
- UAE & Middle East: Rising awareness and demand for traditional grains among health-conscious consumers.
- Japan & South Korea: Strong demand due to their preference for functional foods and ancient grains.
Major Competitors in the Millet Export Industry
The millet export market is competitive, with several key players dominating the space. Competitors can be categorized into large corporations, government-backed cooperatives, and small-scale organic exporters.
Key Players in the Millet Export Market
- ITC Limited (India): One of the largest exporters of agricultural products, including millets. They have an established global supply chain and strong branding.
- Shree Sheela International (India): Specializes in organic millet exports, supplying to major markets in the USA, Canada, and Europe.
- 24 Mantra Organic (India): A well-known organic brand that exports a variety of millet-based products.
- Ardent Mills (USA): A major grain supplier that has entered the millet market due to increasing demand.
- Navadarshanam (India): A small-scale organic millet supplier with a niche market in premium health-conscious consumers.
Small-Scale Exporters
In addition to large corporations, many small and mid-sized companies export millets, often specializing in organic and premium-grade products. These exporters differentiate themselves through:
- Unique product offerings (organic, gluten-free, value-added millets like millet flour and snacks).
- Direct-to-consumer sales through e-commerce and international retail partnerships.
- Sustainable and ethical sourcing practices that appeal to conscious consumers.
Pricing Strategies in Millet Exports
Pricing in the millet export business depends on several factors:
- Production Costs: Includes farming, harvesting, and processing costs.
- Quality of Millets: Organic and premium-grade millets fetch higher prices.
- Market Demand: Prices fluctuate based on global demand, supply shortages, and trade policies.
- Logistics and Tariffs: Export duties, shipping costs, and customs regulations impact pricing.
Pricing Trends
- Bulk export prices for millets typically range between $500 to $1,200 per metric ton, depending on quality and type.
- Organic millets command a 20-30% premium over conventional varieties.
- Processed millet products (flour, flakes, ready-to-cook) have higher profit margins compared to raw millets.
Competitive Pricing Strategies
- Cost-Plus Pricing: Adding a profit margin over production and logistics costs.
- Market-Based Pricing: Adjusting prices based on competitor rates and customer expectations.
- Value-Based Pricing: Charging premium rates for organic or processed millet products.
- Volume Discounts: Offering discounts for bulk purchases to attract large buyers.
Supply Chain & Logistics in Millet Export
Key Supply Chain Components
The millet export supply chain involves multiple stages, from sourcing to final delivery:
Sourcing & Farming:
-
- Establishing contracts with millet farmers or cooperatives ensures a steady supply.
- Organic certification and quality control checks are necessary for premium markets.
Processing & Packaging:
-
- Cleaning, grading, and processing (e.g., making millet flour or flakes) enhance product value.
- Packaging must meet international standards, ensuring long shelf life and compliance with regulations.
Storage & Warehousing:
-
- Proper storage in moisture-free environments prevents spoilage.
- Cold storage may be required for processed millet products.
Shipping & Logistics:
-
- Choosing the right shipping method (air, sea, or land) based on costs and delivery timelines.
- Ensuring smooth customs clearance and adherence to export regulations.
Challenges in the Supply Chain
- Price Fluctuations: Changes in production costs or global demand can impact profitability.
- Quality Control: Maintaining consistent quality across shipments is crucial.
- Regulatory Compliance: Each country has different import regulations and food safety standards.
Optimizing the Supply Chain
- Partnering with reliable logistics providers to reduce transit times.
- Investing in modern processing technology to maintain quality.
- Using blockchain or traceability tools for better supply chain transparency.
How to Position Yourself Against Competitors
To compete successfully in the millet export business, exporters need a strong value proposition. Here are some key strategies:
Focus on Organic and Premium Quality
- Certifications: Obtain organic, non-GMO, and food safety certifications (FSSAI, APEDA, USDA Organic, EU Organic).
- Traceability: Provide farm-to-table transparency through QR codes or blockchain tracking.
Product Diversification
- Instead of just exporting raw millet grains, offer value-added products like:
- Millet flour
- Ready-to-cook millet meals
- Millet-based snacks and energy bars
Strong Branding & Marketing
- Build a strong online presence through digital marketing, social media, and B2B platforms like Alibaba.
- Highlight sustainability and health benefits in branding.
- Participate in international trade fairs and expos to connect with global buyers.
Competitive Pricing & Reliable Supply
- Offer competitive bulk pricing without compromising quality.
- Maintain consistent supply chains by working with multiple farmers and suppliers.
Build Long-Term Partnerships
- Establish strong relationships with wholesalers, retailers, and distributors in key markets.
- Offer customized packaging and branding for clients looking for private labeling.
Steps to Start a Millet Export Business
1. Register Your Business
To operate legally, you must register your millet export business with the following:
- Obtain a business license
- Register under the Import-Export Code (IEC) issued by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) in India
- Get a GST registration
2. Select the Right Type of Millet for Export
Different millets cater to diverse international markets. Some of the most exported millets include:
- Foxtail Millet
- Pearl Millet
- Finger Millet (Ragi)
- Sorghum (Jowar)
- Barnyard Millet
- Little Millet
3. Sourcing Quality Millets
Partner with certified farmers or millet-producing cooperatives to source high-quality, chemical-free millets. Ensuring proper storage and packaging is crucial to maintaining freshness during shipping.
4. Comply with Export Regulations
Meeting international quality standards is critical for the millet export business. Necessary certifications include:
- FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India)
- APEDA (Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority)
- USDA Organic Certification (for organic millet exports)
- EU Organic Certification (for exports to European countries)
5. Finding International Buyers
Exporters can find buyers through:
- Export Promotion Councils (such as APEDA)
- B2B Platforms (Alibaba, Indiamart, TradeIndia)
- International Food Expos
- Networking with Importers and Distributors
Millet Export Pricing and Cost Factors
1. Determining Millet Export Prices
The pricing of millets depends on factors such as:
- Millet type and quality
- Market demand
- Packaging and transportation costs
- Custom duties and taxes
2. Cost of Exporting Millets
Key cost components in the millet export business include:
- Procurement costs
- Processing and packaging
- Freight and logistics
- Customs clearance and documentation
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
1. Packaging and Labeling
Proper packaging ensures that millets retain their quality during transit. Use:
- Airtight, moisture-proof packaging
- Labeling as per import country’s guidelines
2. Shipping and Logistics
Choose cost-effective shipping methods such as:
- Sea freight for bulk exports
- Air freight for smaller, high-value shipments
Marketing and Branding Your Millet Export Business

1. Creating an Online Presence
A strong digital presence helps attract global buyers. Essential steps include:
- Developing a professional website
- Using SEO strategies to rank for “millet export business”
- Leveraging social media platforms
2. Participating in Trade Shows and Expos
Attending international food expos increases brand visibility and helps connect with potential buyers.
Challenges in the Millet Export Business
1. Quality Control Issues
Maintaining consistent quality across shipments is essential for building a reputable brand.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Each country has specific import regulations that must be adhered to avoid rejection of shipments.
3. Logistics and Transportation
Ensuring timely delivery while minimizing costs can be challenging, especially for bulk exports.
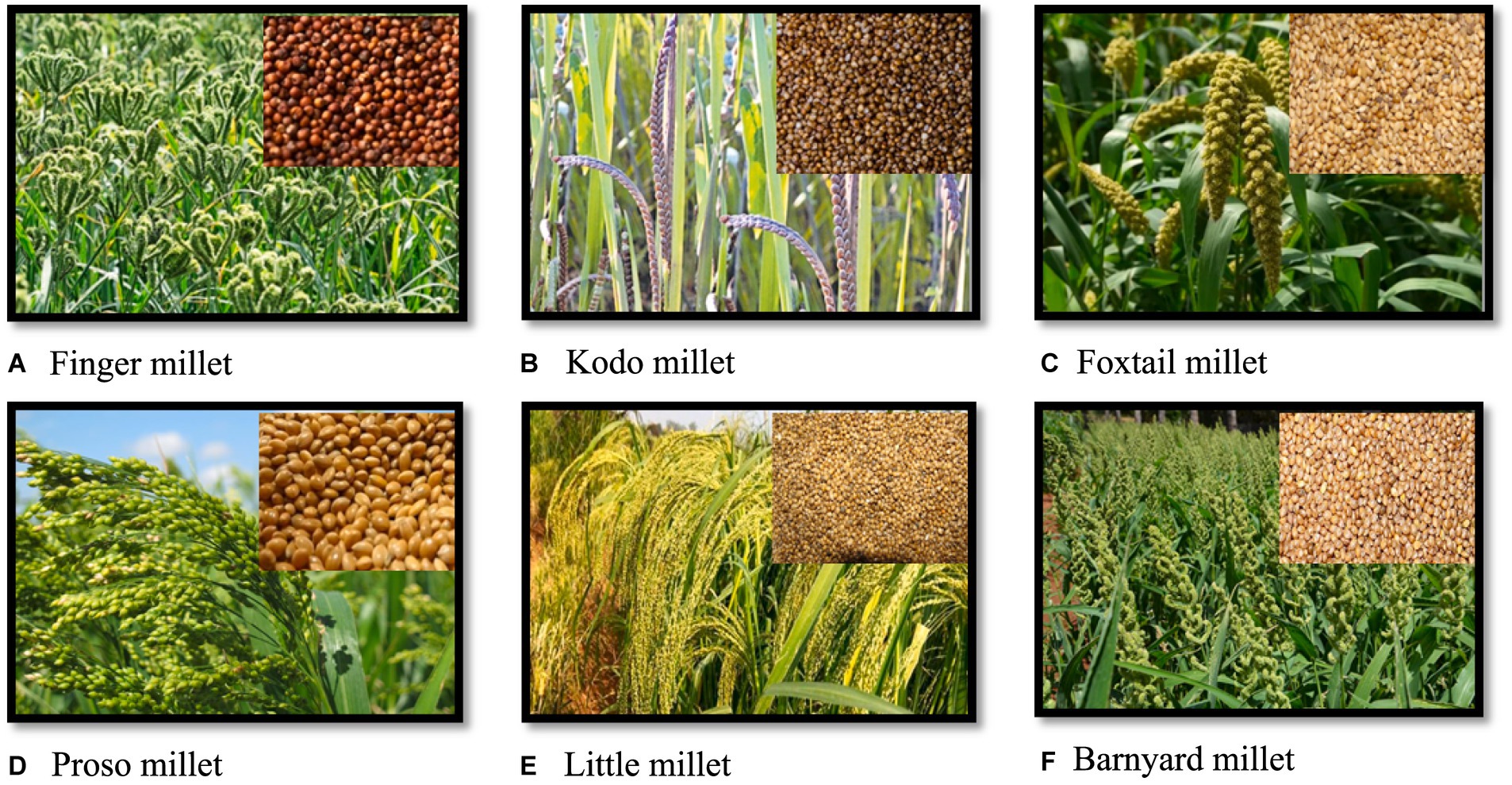

Future Trends in Millet Export Business
1. Rising Demand for Organic Millets
Consumers are shifting towards organic food, increasing the demand for certified organic millets.
2. Expansion in New Markets
African and Middle Eastern countries are emerging as new markets for millet imports.
3. Government Support and Policies
Government initiatives such as subsidies and incentives for millet farming will further boost the millet export business.
Conclusion
Starting a millet export business requires thorough market research, compliance with regulations, and efficient supply chain management. By leveraging digital marketing, networking with international buyers, and maintaining high-quality standards, entrepreneurs can successfully establish themselves in the global millet market.
FAQ: How to Start a Millet Export Business
1. What are the key steps to start a millet export business?
To start a millet export business, follow these steps:
- Market Research: Identify demand, target countries, and competitor analysis.
- Business Registration: Register your company, obtain GST, IEC (Import-Export Code), and APEDA certification.
- Sourcing Millets: Partner with reliable farmers or suppliers to ensure a consistent supply.
- Processing & Packaging: Invest in cleaning, grading, and packaging to meet global quality standards.
- Compliance & Certification: Get necessary certifications like FSSAI, USDA Organic (if required), and country-specific approvals.
- Logistics & Shipping: Arrange reliable transportation and adhere to export regulations.
- Marketing & Sales: Build an online presence, connect with global buyers, and list on B2B platforms like Alibaba.
2. What certifications are required for millet exports?
Certifications depend on the target country. The most common ones include:
- FSSAI (India): Mandatory for food businesses in India.
- APEDA Certification: Required for exporting agricultural products from India.
- Import-Export Code (IEC): Issued by DGFT for international trade.
- USDA Organic / EU Organic: If exporting organic millets.
- HACCP & ISO 22000: Food safety and quality management certifications.
3. Which countries have high demand for millets?
Millets are in demand in:
- USA & Canada: Due to the growing trend of gluten-free and organic foods.
- Europe (Germany, France, UK): Consumers prefer sustainable and nutritious grains.
- UAE & Middle East: Health-conscious communities are shifting to millets.
- Japan & South Korea: Used in traditional and functional foods.
4. How can I source high-quality millets for export?
You can source millets from:
- Local farmers and cooperatives with organic and sustainable farming practices.
- Agro-trade markets in millet-producing states like Rajasthan, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Government-registered FPOs (Farmer Producer Organizations) for bulk sourcing.
5. How do I determine pricing for exported millets?
Millet export pricing depends on:
- Type & Quality: Organic millets fetch a higher price than regular ones.
- Processing Costs: Cleaning, grading, and packaging impact final pricing.
- Market Demand: Prices fluctuate based on international trends and supply chain factors.
- Logistics & Tariffs: Export duties, shipping, and customs costs affect pricing.
6. How can I find international buyers for millets?
You can find buyers through:
- B2B Marketplaces: Alibaba, IndiaMART, TradeIndia, ExportHub.
- Trade Fairs & Expos: Participate in food and agriculture expos.
- Export Promotion Councils: APEDA and Chamber of Commerce events.
- Social Media & Digital Marketing: Use LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram to connect with potential buyers.
7. What are the common challenges in millet exports?
- Quality Control: Meeting international food safety standards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have different import rules.
- Logistics & Shipping: Finding cost-effective and reliable transportation.
- Competition: Competing with established exporters and pricing pressures.
8. What are the best packaging practices for millet exports?
- Use airtight, moisture-proof packaging to prevent spoilage.
- Comply with FDA or EU food packaging standards if exporting to the US or Europe.
- Include clear labeling with product details, expiry date, and certifications.
9. How long does it take to start exporting millets?
Setting up a millet export business can take 3 to 6 months, depending on:
- Registration and certification processes.
- Sourcing and supply chain setup.
- Finding buyers and setting up logistics.
10. How much investment is required to start a millet export business?
The investment depends on the scale of business:
- Small-Scale Exporter: ₹5-10 lakhs ($6,000 – $12,000) for sourcing, certification, and initial shipments.
- Medium-Scale Exporter: ₹20-50 lakhs ($25,000 – $60,000) for larger storage and processing facilities.
- Large-Scale Exporter: ₹1 crore+ ($120,000+) for high-volume production and global marketing.