Types of Millets & Their Benefits
Explore various types of millets, their unique benefits, and why they are a superfood. Discover more!
Millets are ancient grains packed with nutrition and have been a staple food in many parts of the world for centuries. They are drought-resistant, easy to grow, and offer numerous health benefits. With the increasing awareness of healthy eating, millets are making a comeback in modern diets. But did you know that there are several types of millets, each with unique properties and benefits? In this article, we’ll explore Different Types of Millets and why they should be a part of your diet.
What Are Millets?

Millets are small-seeded grasses that are widely grown as cereal crops or grains for human consumption and fodder. They are naturally gluten-free and rich in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals. They can be classified into two main categories: major millets and minor millets.
Major Millets

1. Pearl Millet (Bajra)
Pearl millet is one of the most widely grown millets across the world, particularly in India and Africa. It is rich in fiber, iron, magnesium, and protein. This millet helps in improving digestion, boosting energy levels, and managing diabetes. Bajra is commonly used in making rotis, porridge, and fermented foods like khichdi and bhakri.
2. Finger Millet (Ragi)
Finger millet, also known as ragi, is a powerhouse of calcium and amino acids. It is an excellent choice for growing children, pregnant women, and the elderly as it helps in strengthening bones and preventing osteoporosis. Due to its low glycemic index, it is beneficial for diabetics. Ragi is often used to prepare porridge, dosas, laddoos, and malt drinks.
3. Sorghum (Jowar)
Sorghum, or jowar, is another widely consumed millet, known for its high protein, antioxidants, and dietary fiber content. It aids in heart health, improves digestion, and helps lower cholesterol levels. Jowar flour is used to make rotis, bread, and various baked goods.
4. Foxtail Millet (Kangni/Korra)
Foxtail millet is rich in carbohydrates, protein, and dietary fiber. It is an excellent food for weight management, heart health, and diabetes control. Foxtail millet is commonly used to prepare upma, pongal, and porridge, making it a versatile grain for daily consumption.
Minor Millets
5. Little Millet (Kutki/Samai)
Little millet is a great alternative to rice due to its high fiber and antioxidant content. It aids digestion, strengthens the immune system, and provides long-lasting energy. It is commonly used in making idlis, dosas, and rice-based dishes.
6. Barnyard Millet (Sanwa/Jhangora)
Barnyard millet is a low-calorie grain, making it an ideal choice for weight loss. It is also high in iron and fiber, which helps maintain good digestion and prevents anemia. This millet is commonly used to prepare khichdi, porridge, and kheer.
7. Kodo Millet (Kodra)
Kodo millet is rich in antioxidants and dietary fiber, making it an excellent choice for reducing blood sugar levels and cholesterol. It helps in detoxification and supports heart health. Kodo millet is often used in making rotis, rice dishes, and various traditional snacks.
8. Proso Millet (Chena/Barri)
Proso millet is a protein-rich grain with a low glycemic index, making it ideal for diabetics and heart patients. It also provides essential amino acids, aiding in muscle growth and repair. Proso millet is commonly used in soups, bread, and porridge.
9. Browntop Millet (Korale)
Browntop millet is rich in fiber and essential minerals, helping in detoxification and maintaining gut health. It supports digestion and is known to prevent constipation. This millet is often used to prepare dosas, upma, and healthy salads.
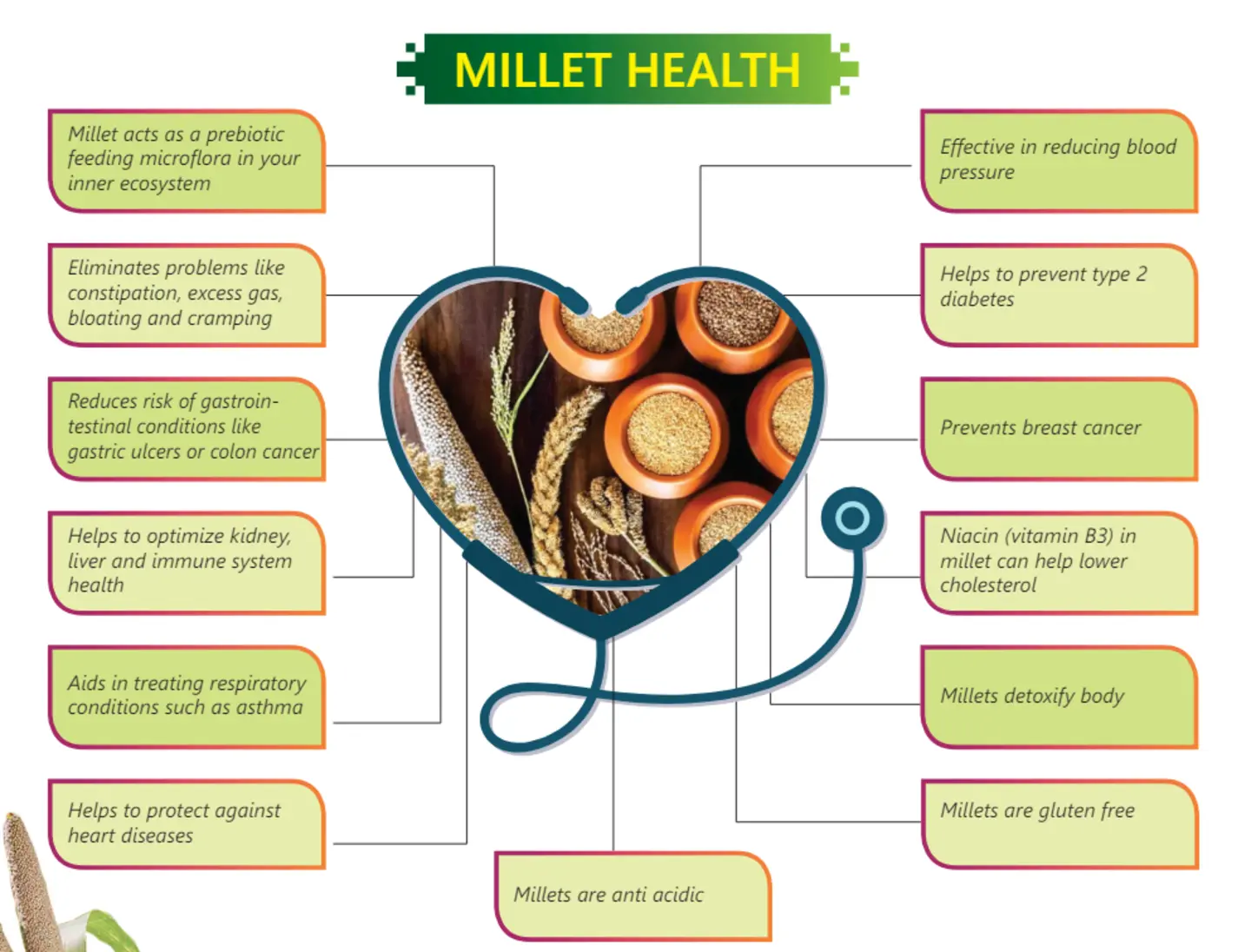
Health Benefits of Millets

1. Rich in Nutrients
Millets are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote overall health. They provide magnesium, calcium, iron, and B vitamins, which support brain function, heart health, and energy production.
2. Gluten-Free
Unlike wheat and other common grains, millets are naturally gluten-free, making them suitable for people with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
3. Good for Digestion
The high fiber content in millets aids digestion, prevents constipation, and promotes a healthy gut microbiome.
4. Helps in Weight Management
Since millets are low in calories and high in fiber, they keep you full for longer, reducing hunger cravings and aiding in weight loss.
5. Controls Blood Sugar Levels
Millets have a low glycemic index, which means they release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent spikes.
How to Include Millets in Your Diet?

- Replace rice with millet in daily meals for a healthier option.
- Use millet flour in rotis, bread, pancakes, and baked goods.
- Make porridge or breakfast cereals using different millets.
- Try millet-based snacks like laddoos, crackers, and khichdi.
Conclusion
Millets are an excellent addition to a healthy diet. They provide numerous health benefits, are easy to cook, and are highly versatile. By incorporating Different Types of Millets into your meals, you can enjoy both taste and nutrition while making a sustainable food choice.
FAQs
1. Which millet is best for weight loss?
Barnyard millet and foxtail millet are excellent choices for weight loss due to their low-calorie and high-fiber content.
2. Can diabetics eat millets?
Yes, millets like finger millet, foxtail millet, and kodo millet have a low glycemic index and help regulate blood sugar levels.
3. How can I cook millets?
Millets can be cooked like rice, made into porridge, ground into flour for baking, or used in snacks and breakfast dishes.
4. Are millets better than rice and wheat?
Millets are more nutrient-dense, have higher fiber content, and are gluten-free, making them a healthier alternative to rice and wheat.
5. Where can I buy millets?
Millets are available in supermarkets, organic stores, and online grocery platforms.